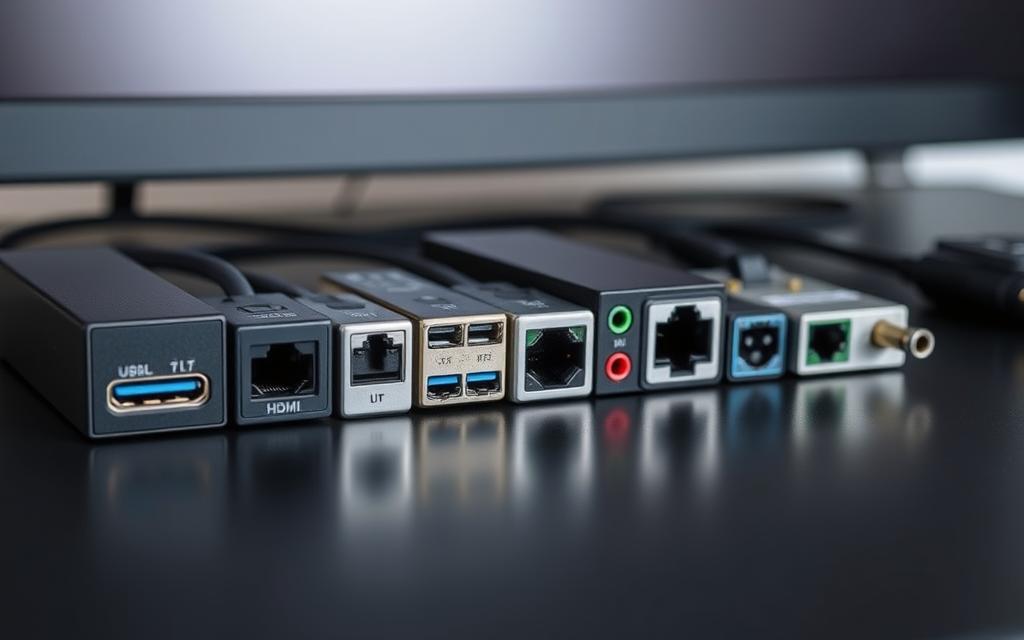
Ports of a PC Explained for Non-Techies
Understanding the various ports on your computer is crucial for maximising its functionality. In today’s digital age, computers are used for a multitude of tasks, from work and entertainment to education and communication.
As we increasingly rely on our PCs and laptops, knowing how to connect external devices becomes essential. This guide aims to demystify the different types of computer ports, explaining their purposes and how they facilitate data transfer and expanded functionality.
By understanding the connection options available on your computer, you can enhance your overall computing experience. Whether you’re looking to transfer files, connect peripherals, or simply understand the capabilities of your PC, this guide provides a comprehensive overview in straightforward, jargon-free language.
Understanding Computer Ports: The Basics
Understanding computer ports is fundamental to appreciating how data is transferred between devices. Computer ports serve as interfaces between a computer and external or internal devices, facilitating various functions from data transfer to charging.
What Is a Computer Port?
A computer port is defined as a “connection point or interface between a computer and an external or internal device.” In simpler terms, ports allow users to connect different devices to their laptop or desktop, enhancing the computer’s functionality.
Why Computer Ports Matter
Computer ports are crucial for several reasons. They determine the range of external devices that can be connected, directly affecting the system’s versatility and functionality. The right ports enable the connection of essential peripherals like printers, external monitors, and storage devices. Moreover, ports facilitate data transfer between the computer and other devices, making tasks like file sharing and multimedia display possible.
| Port Type | Function | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| USB | Data Transfer and Charging | Connecting peripherals like flash drives and printers |
| HDMI | Video and Audio Output | Connecting to external monitors or TVs |
| Ethernet | Network Connection | Establishing a wired internet connection |
Understanding the ports available on your computer helps in making informed decisions when purchasing accessories or peripheral devices. For non-technical users, knowing the basics of port functionality can save time and frustration when setting up computer systems or troubleshooting connection issues.
The Evolution of PC Ports
The PC port landscape has undergone significant transformations over the years. The types of ports available have changed to accommodate new technologies and user requirements, impacting how we interact with our devices.
From Legacy Ports to Modern Connections
The journey from legacy ports to modern connections has been marked by significant advancements. The humble 3.5 mm jack, for instance, has its roots in the quarter-inch technology used by telephone operators in the 1870s. Modern ports have evolved to offer faster data transfer rates and greater versatility.
How Port Technology Has Advanced
Port technology has seen dramatic improvements in terms of speed and functionality. Modern ports like USB-C are smaller yet more capable than their predecessors, offering faster data transfer and power delivery. The integration of multiple functions into single ports has been a significant advancement, enhancing user convenience and device compatibility.
USB Ports: The Universal Connectors
In the world of computer hardware, few connectors have achieved the ubiquity and versatility of the USB port. USB ports have become an indispensable part of modern computing, allowing users to connect a wide range of devices to their PCs.
USB Type-A: The Classic Standard
USB Type-A is the most recognisable USB connector, characterised by its rectangular shape. It remains widely used for connecting devices such as flash drives, keyboards, and mice. The USB Type-A connector is often associated with USB 2.0 and 3.0 standards.
USB Type-B and Mini/Micro Variants
USB Type-B connectors are typically used for larger devices like printers and scanners. Mini and Micro USB variants offer smaller alternatives for mobile devices. These connectors are designed for specific applications where size and power requirements differ.
USB Type-C: The Modern All-in-One
USB Type-C represents the latest generation of USB technology, offering faster speeds and reversible design. It is becoming increasingly popular as a universal port for both data transfer and power delivery. USB Type-C is expected to replace earlier USB types in future devices.
Understanding USB Speeds
USB speeds vary significantly across different generations. USB 2.0 offers speeds up to 480 Mbps, while USB 3.0 increases this to 5 Gbps. USB 3.1 Gen 2 further accelerates data transfer to 10 Gbps. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right cables and devices for specific tasks.
Video Display Ports Explained
The type of video display port used can significantly impact the resolution and clarity of the image on your screen. When connecting your PC to a monitor or display device, understanding the different types of video ports is essential.
HDMI: High-Definition Multimedia Interface
HDMI is a widely used interface for transmitting high-definition video and audio signals. It offers high-quality digital transmission, making it ideal for home entertainment systems and modern display devices.
DisplayPort: The Professional Choice
DisplayPort is favoured by professionals for its ability to support high-resolution display setups and multi-monitor configurations. It offers advanced capabilities, including higher refresh rates and greater bandwidth.
VGA and DVI: The Legacy Video Connections
Older systems often use VGA (Video Graphics Array) and DVI (Digital Visual Interface) for video transmission. While VGA is largely outdated, DVI remains in use for certain applications, supporting resolutions up to 2560 x 1600.
Choosing the Right Video Port
Selecting the appropriate video port depends on the capabilities of both your computer and display device. For most users, HDMI offers a convenient balance of quality and compatibility. Professionals may prefer DisplayPort for its advanced features.
Audio Ports and Connections
Understanding audio ports is crucial for connecting various devices to your PC. Audio ports enable you to enjoy high-quality sound from your computer, whether you’re listening to music, watching a movie, or gaming.
The 3.5mm Headphone/Microphone Jack
The 3.5mm jack is one of the most common audio ports found on PCs. It’s used for both headphones and microphones, providing an easy way to connect your audio devices. This port is versatile, supporting various audio configurations.
Digital Audio Ports (S/PDIF)
For superior audio quality, digital audio ports like S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) are used. S/PDIF connects to external devices such as DVD players and home theatre systems, offering improved quality over analog ports. It comes in optical (Toslink connector) and coaxial (RCA connector) forms, supporting multi-channel surround sound formats like Dolby Digital and DTS, making it ideal for speakers and home entertainment systems.
To learn more about audio ports, you can visit this guide for a comprehensive overview.
| Audio Port Type | Description | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| 3.5mm Jack | Analog audio connection | Headphones, Microphones |
| S/PDIF (Optical) | Digital audio connection using light signals | Home theatre systems, Soundbars |
| S/PDIF (Coaxial) | Digital audio connection using electrical signals | DVD players, Home entertainment systems |
Network Ports of a PC
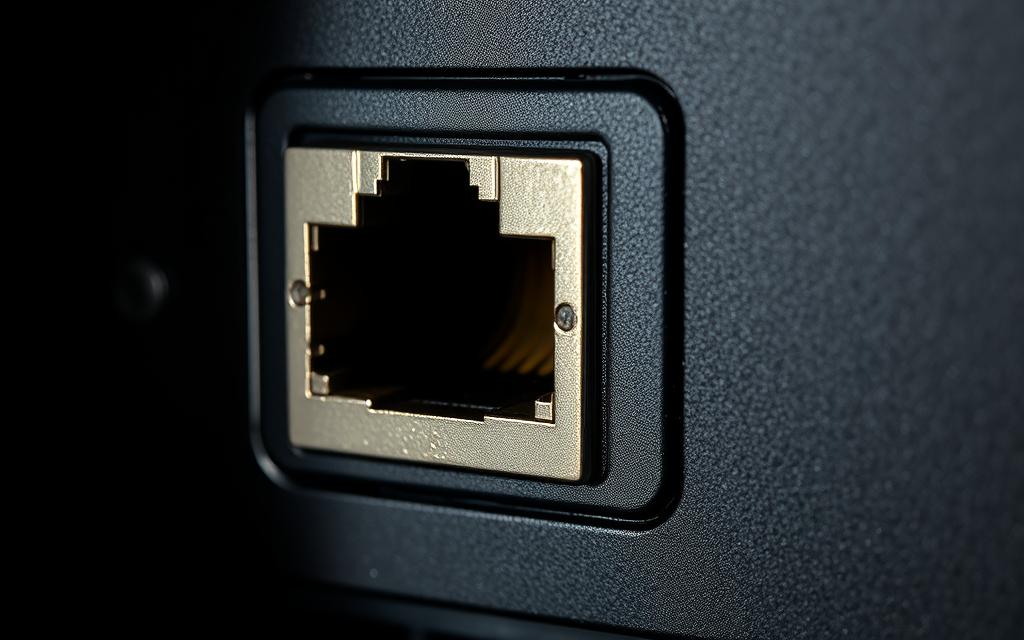

The ethernet port, commonly found on PCs, is a vital component for establishing a stable internet connection. It connects your laptop or PC to a router or modem using the ethernet protocol, typically featuring eight pins to link ethernet cables with a serial data modem.
Ethernet (RJ-45) Connections
Ethernet ports, also known as RJ-45 ports, are interfaces that enable internet-enabled devices to connect to other network devices. They provide a reliable means of transferring data at high speeds, making them ideal for applications that require consistent bandwidth.
Why Wired Connections Still Matter
Despite the prevalence of Wi-Fi, wired ethernet connections remain superior for several reasons. They offer lower latency, making them preferable for online gaming, video conferencing, and real-time applications. Additionally, wired networks are less susceptible to interference and are inherently more secure than wireless networks.
Thunderbolt: The Speed Champion
Thunderbolt technology has revolutionised the way we connect devices to our PCs, offering unparalleled speed and versatility. As a high-speed connection technology, Thunderbolt enables users to transfer data at rates significantly faster than traditional USB connections. This makes it particularly valuable for professionals working with large files, such as video editors and graphic designers.
With its ability to support multiple monitors and high-speed data transfer, Thunderbolt has become an essential feature for many modern laptops. It can carry two DisplayPort signals, allowing it to power two 4K monitors simultaneously.
Capabilities
Thunderbolt 3 and 4 offer a range of advanced capabilities, including support for external graphics processing units (eGPUs) and high-speed data transfer. Thunderbolt 3 can support two 4K displays at 60Hz, making it ideal for productivity-focused workspaces. Additionally, Thunderbolt docking stations can transform a laptop into a complete desktop setup with a single connection cable, supporting multiple monitors, peripherals, and charging.
When to Use Thunderbolt Connections
Thunderbolt connections are particularly useful for professionals who require high-speed data transfer and the ability to connect multiple devices. For instance, video editors can use Thunderbolt to transfer large video files quickly, while graphic designers can connect multiple high-resolution monitors to enhance their productivity. When choosing a type of connection, consider whether you need the high-speed data transfer and multi-display support that Thunderbolt offers.
Memory Card Readers
Memory card readers are a convenient feature in modern computers, allowing users to access data from various memory cards. This feature is particularly useful for expanding a computer’s storage capacity.
SD and MicroSD Card Slots
Many laptops and desktops come equipped with SD and microSD card slots. These slots enable users to insert memory cards directly into their computer, facilitating the transfer of files. For instance, you can expand your laptop’s storage using a microSD card, which is especially useful if your laptop has limited internal storage.
Using Memory Cards with Your Computer
When you insert a memory card into a computer’s card reader, it appears as a removable drive, allowing you to access its contents through your standard file explorer. You can use memory cards for various purposes, including data transfer, backup storage, or even as a performance enhancer with ReadyBoost on compatible Windows systems. It’s essential to safely eject memory cards before removing them to prevent data corruption.
- Memory cards can be used to expand your computer’s storage capacity.
- They can serve multiple purposes, including data transfer and backup storage.
- Safely ejecting memory cards before removal prevents data corruption.
Power Delivery Ports
USB-C is revolutionizing laptop charging by providing a universal power delivery solution. This shift is simplifying the way we power our devices, reducing the clutter of multiple chargers and cables.
Charging via USB-C
Many newer laptops now use USB-C for charging, eliminating the need for proprietary power adapters. This change simplifies the connection ecosystem, making it easier for users to charge their devices with a standard cable.
Traditional Power Connections
Traditional laptop power connections typically use barrel connectors that vary in size and voltage requirements between manufacturers. These proprietary connections often include features like central pins for verifying compatibility between the charger and laptop.
| Connector Type | Voltage Range | Common Use |
|---|---|---|
| Barrel Connector | 12V – 20V | Laptop Charging |
| USB-C | 5V – 20V | Universal Charging |
Legacy Ports You Might Still Encounter
Legacy ports, though largely outdated, can still be found on some PCs and peripherals. These older ports were once the standard for connecting various devices to computers.
Serial and Parallel Ports
Serial and parallel ports were used for connecting older peripherals. Serial ports transferred data one bit at a time, while parallel ports transferred multiple bits simultaneously, offering faster transfer rates for certain devices.
PS/2 Ports for Keyboard and Mouse
PS/2 ports were used for connecting keyboards and mice. They were once the standard, but have largely been replaced by USB connections, which offer greater versatility and speed.
FireWire (IEEE1394)
FireWire, also known as IEEE1394, was a high-speed interface for connecting digital devices, particularly popular for video cameras and external hard drives. It offered faster data transfer rates compared to USB 2.0, making it ideal for applications requiring high-bandwidth data transfer.
| Legacy Port | Primary Use | Notable Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Serial Port | Connecting older peripherals | Transferred data one bit at a time |
| Parallel Port | Connecting printers and scanners | Transferred multiple bits simultaneously |
| PS/2 Port | Connecting keyboards and mice | Replaced by USB |
| FireWire (IEEE1394) | Connecting digital devices | High-speed data transfer |

Identifying Ports on Your PC
When setting up your PC, understanding the layout of its ports is crucial. This knowledge helps in connecting peripherals and accessories efficiently.
Common Port Locations on Desktops
Desktop PCs typically have their ports located at the back, with some models offering additional ports on the front or sides for easier access. The rear ports usually include USB ports, audio jacks, and video outputs like HDMI or DisplayPort. Understanding the design of your desktop’s port layout can simplify connecting devices.
| Port Type | Common Location |
|---|---|
| USB Ports | Back, Front |
| Audio Jacks | Back, Front |
| Video Outputs | Back |
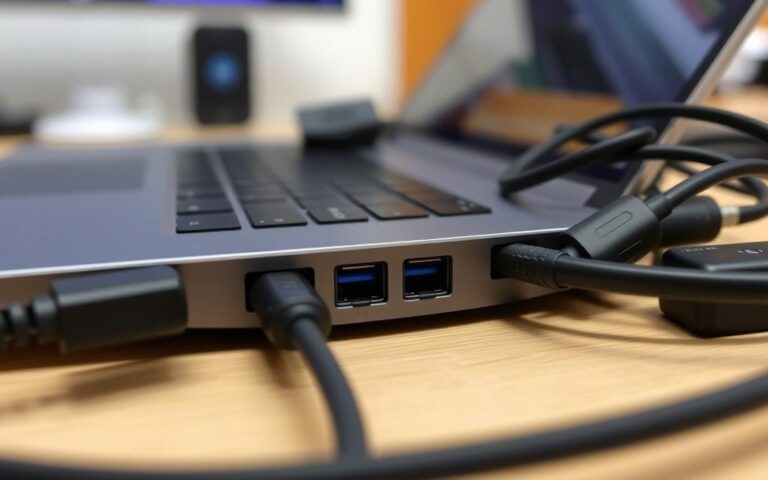
Port Layouts on Laptops
Laptop port layouts vary significantly between models, with a trend towards fewer ports in newer, thinner designs. Ports are distributed around the available edges, with power and video outputs often on the sides or rear. Commonly used connections like USB ports are positioned for easy access. Business-oriented laptops often offer more comprehensive port selections than consumer models.
- Laptops distribute ports around their edges for accessibility.
- Ultraportable laptops may sacrifice port variety for thin design.
- Business laptops typically offer more ports than consumer models.
Port Hubs and Docking Stations
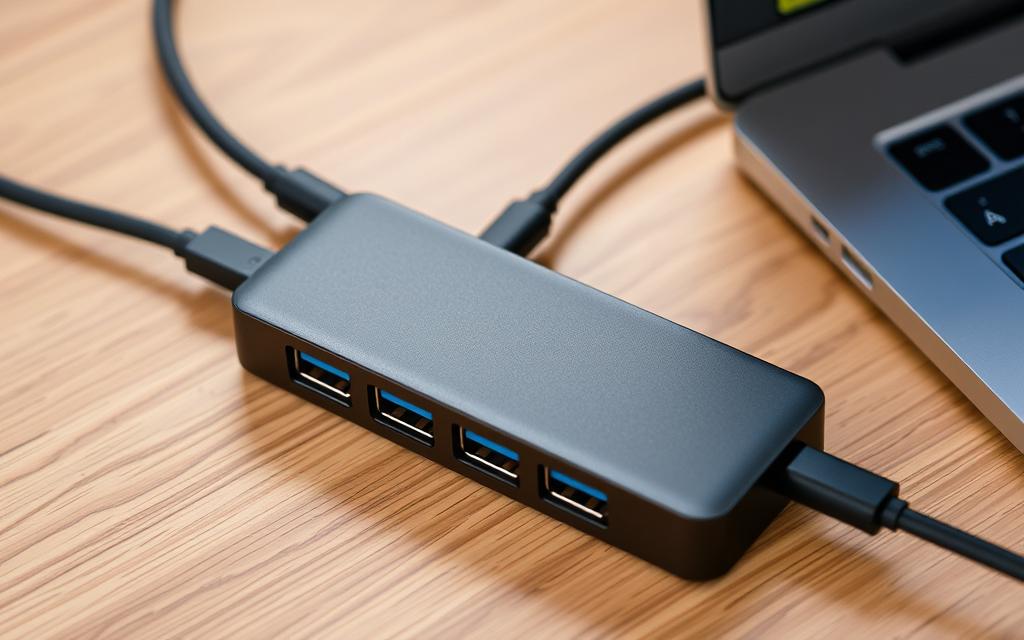

As the number of devices we use continues to grow, the need for more ports on our computers becomes increasingly apparent. Port hubs and docking stations offer a practical solution to this problem, allowing users to expand their PC’s connectivity options.
Expanding Your Port Options
Port hubs and docking stations enable users to connect multiple devices to their computer, enhancing productivity and flexibility. For instance, the IOGEAR HUB-C – USB-C to 4-port USB-A Hub is ideal for connecting peripherals to a laptop with limited ports.
Choosing the Right Hub for Your Needs
When selecting a hub or docking station, consider both current and future data transfer needs. Key considerations include the type of USB ports (e.g., USB-A, USB-C) and the hub’s ability to transfer data at sufficient speeds. For data-intensive applications, look for hubs that support the fastest standards your computer can handle.
- Consider both current and future connectivity needs.
- Distinguish between hubs and docking stations based on your requirements.
- Ensure compatibility, particularly with USB-C hubs.
Troubleshooting Common Port Issues
Troubleshooting common port issues can be a straightforward process if you know the right steps to take. When your computer ports stop responding, it can disrupt your workflow. Understanding how to diagnose and fix these issues is essential.
When Ports Don’t Respond
If your ports are not responding, try disconnecting all devices and restarting your computer. Then, reconnect one device at a time to identify the problematic one. For USB ports, try using different ports to see if the issue is with the port or the device itself.
Fixing Connection Problems
To fix connection problems, check your cable for damage. Sometimes, a faulty cable can cause connectivity issues. Ensure your system is updated, as updates often include fixes for connection problems. For persistent USB ports issues, check the USB power settings in your computer’s BIOS/UEFI to ensure they are not disabled or underpowered.
The Future of Computer Ports
The future of computer ports is rapidly evolving with advancements in technology. As we move towards a more wireless world, the need for physical ports is diminishing. However, this shift also brings about new opportunities for improved data transfer and connectivity.
Wireless Connections and Port Reduction
With the rise of Bluetooth headsets and other wireless devices, the reliance on traditional ports is decreasing. This trend is expected to continue, with wireless connections becoming increasingly prevalent. The reduction in ports is also driven by the adoption of USB-C and other multi-purpose ports.
Emerging Port Technologies
Several emerging technologies are set to revolutionize computer ports. These include:
- USB4, which offers speeds up to 40 Gbps, building on Thunderbolt technology for enhanced speed.
- Optical connection technologies that promise faster data transfer with lower power consumption.
- Modular port systems that could allow devices to be customized with the required connections.
As these technologies mature, they will shape the future of computer connectivity.
Practical Tips for Using PC Ports Effectively
Understanding how to use your PC’s ports effectively is crucial for a seamless computing experience. To get the most out of your computer’s connectivity options, consider a few practical strategies.
Organising your workspace is key. Connect frequently used devices to easily accessible ports, reserving rear or less convenient connections for permanent peripherals like your keyboard. Labelling cables, particularly when using adapters or hubs, simplifies troubleshooting and reconfiguration of your setup.
- Invest in quality cables and adapters from reputable manufacturers to avoid intermittent issues and potential damage to your ports.
- When travelling with a laptop, a single multi-port adapter is often more practical than carrying multiple single-purpose adapters.
- Protect unused ports with dust covers, especially in industrial or dusty environments, to prevent debris accumulation.
Consider the power requirements of USB devices, as connecting too many power-hungry peripherals to unpowered hubs can lead to unstable connections. For desktop computers, front panel ports are convenient but may provide slower data transfer than direct motherboard connections at the rear.
Conclusion
In today’s digital age, comprehending the various ports on your computer is crucial for optimising your device’s performance and connectivity. Understanding the different types of ports empowers you to make the most of your device’s capabilities without requiring deep technical knowledge.
- The evolution of computer ports reflects broader technological trends toward faster data transfer and greater versatility.
- Familiarity with both legacy and modern ports helps bridge the gap between older and newer technologies, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of devices.
- For most users, focusing on USB, HDMI, and audio connections provides sufficient knowledge for everyday computing tasks on their laptop or computer.
As technology continues to evolve, the trend toward fewer, more versatile ports like USB-C suggests a future where connectivity becomes increasingly standardised and simplified. A basic understanding of ports helps you make informed decisions when setting up a new computer, troubleshooting connection issues, or planning a technology purchase.
FAQ
What is the difference between USB 2.0 and USB 3.0?
USB 3.0 offers significantly faster data transfer speeds of up to 5 Gbps, whereas USB 2.0 has a maximum speed of 480 Mbps, making USB 3.0 more suitable for transferring large files.
Can I use an HDMI port to connect my laptop to a monitor?
Yes, HDMI ports are commonly used to connect devices to monitors or TVs, providing high-definition video and audio signals.
What is the purpose of an Ethernet port on a computer?
An Ethernet port, also known as an RJ-45 port, is used for establishing a wired internet connection, offering a stable and fast network link.
How do I know which type of USB port my device has?
You can identify the type of USB port by its shape and the symbol next to it; for example, USB Type-C has a reversible connector and is often marked with a ‘C’ symbol.
Can I charge my laptop using a USB-C port?
Yes, many modern laptops support charging via USB-C, provided the port is configured for power delivery and the charger is compatible.
What is the difference between DisplayPort and HDMI?
DisplayPort and HDMI are both used for video output, but DisplayPort can support multiple monitors from a single port and is often preferred in professional settings.
Why is my USB device not recognised by my computer?
This could be due to a faulty USB port, incorrect drivers, or a problem with the device itself; try troubleshooting by checking the connection, updating drivers, or testing the device on another computer.
Can I use a USB hub to expand my computer’s port options?
Yes, USB hubs can be used to add more USB ports to your computer, allowing you to connect multiple devices simultaneously.
What is Thunderbolt 3, and how does it differ from USB-C?
Thunderbolt 3 is a high-speed interface that uses the USB-C connector, offering speeds of up to 40 Gbps, whereas standard USB-C speeds are typically up to 10 Gbps; Thunderbolt 3 is designed for demanding applications like data transfer and display connectivity.
How do I identify the ports on my laptop or desktop?
Ports are usually labelled with symbols or icons indicating their function; you can also refer to your device’s documentation or manufacturer’s website for specific information on port configurations.