What is a DC Port on a Computer Monitor Mean: Explained
The DC port is a crucial component on most monitors, serving as the primary power inlet. Unlike other ports that transmit data, such as HDMI or DisplayPort, the DC port supplies power to the device.
A power adapter is used to convert AC power from a wall outlet into DC power that the monitor can use. The DC port is typically marked with a specific symbol or label, making it easily identifiable.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the technical aspects of DC power delivery, including voltage requirements and the role of power adapters. By understanding the DC port and its function, you’ll be better equipped to set up your monitor, troubleshoot power issues, and ensure compatibility when replacing power adapters.
Understanding DC Ports on Computer Monitors
Understanding the purpose of a DC port is essential for using a computer monitor effectively. A DC port is a critical component that allows a monitor to receive the power it needs to operate.
Definition and Basic Function
A DC port is defined as a power input port designed to receive direct current (DC) from an adapter, allowing your monitor to function properly. This definition highlights the primary role of DC ports in delivering power to monitors.
The basic function of a DC port on a computer monitor is to serve as the primary power input connection, accepting electrical current from external power adapters. Unlike data ports that transmit video and audio signals, DC ports are solely responsible for delivering power to the monitor’s internal components.
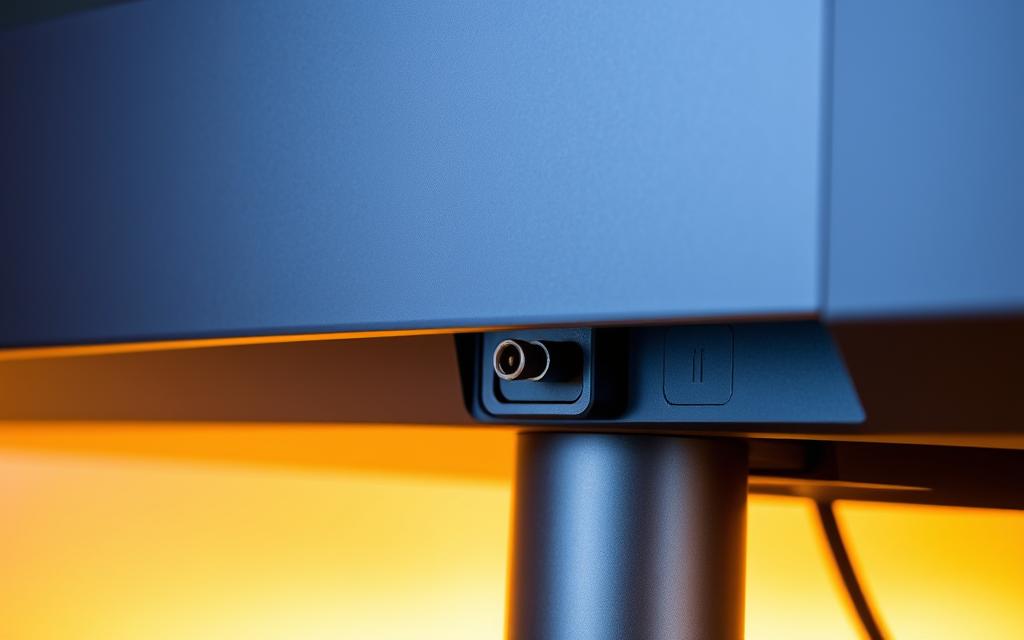
The DC port receives direct current electricity, which is the type of power that electronic devices require for operation. Most monitors feature a circular DC port with a center pin that makes contact with the corresponding power adapter connector.
- DC ports are designed with specific voltage and amperage requirements that must be matched by the power adapter to ensure proper monitor operation.
- Understanding the basic functionality of DC ports helps users distinguish between power and data connections when setting up or troubleshooting monitor issues.
By recognizing the importance of DC ports and their role in powering monitors, users can better appreciate the intricacies of their devices. Proper use and maintenance of DC ports can lead to optimal performance and longevity of computer monitors.
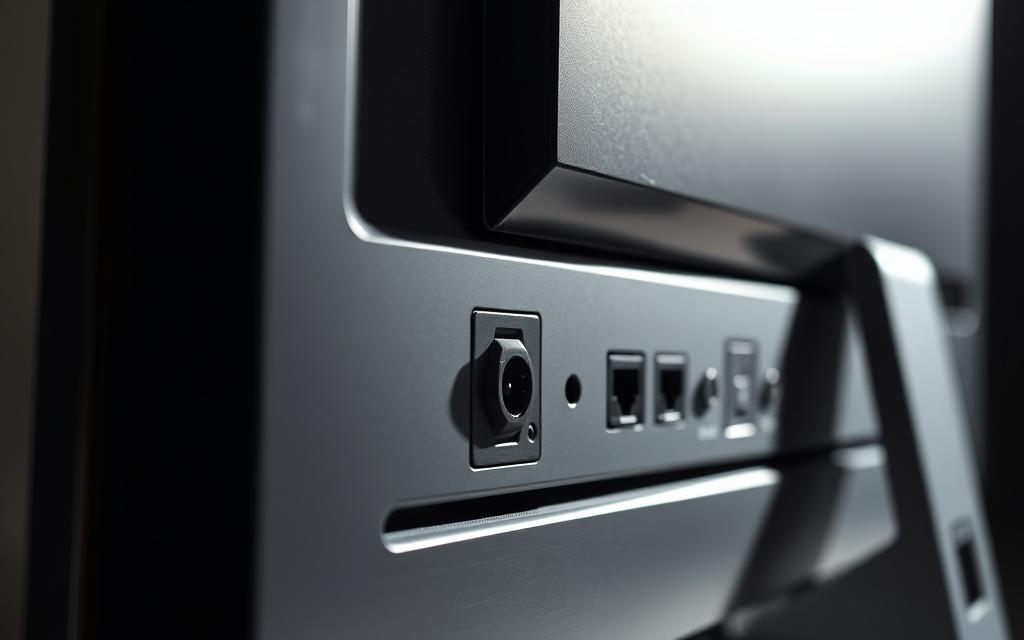
How to Identify a DC Port on Your Monitor
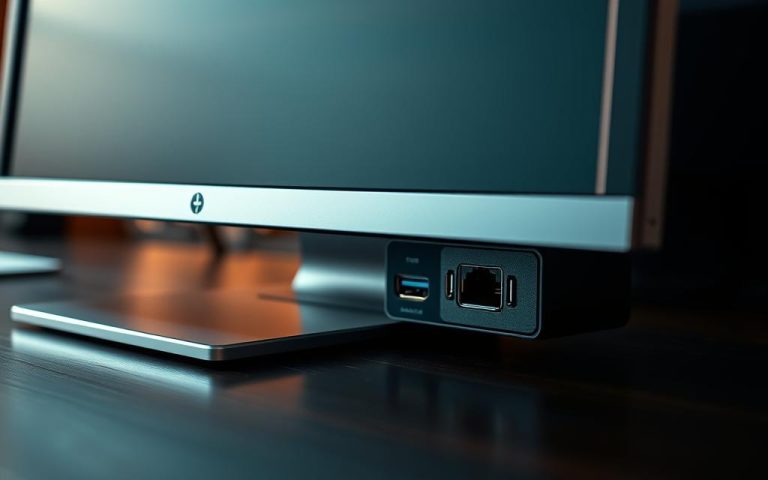
To understand how to power your monitor correctly, you first need to locate and identify its DC port. The DC port is a crucial component for providing power to your monitor, and it’s usually found on the back or rear panel of the device.

Physical Characteristics and Markings
DC ports on computer monitors have distinct physical characteristics that make them identifiable. They are typically circular in shape and may feature a small central pin. The size of these ports can vary, usually ranging from 2.5mm to 5.5mm in diameter, depending on the types of monitors and their power requirements.
The DC port is often labeled with clear markings such as “DC IN” or “POWER,” along with symbols indicating power input specifications. These markings are crucial for identifying the port correctly and ensuring that you use the correct power adapter.
- The DC port is usually located near other ports on the back of the monitor.
- It has a round shape and is sometimes slightly recessed into the monitor’s body.
- Look for text like “DC” or symbols showing power input specifications near the port.
- The connector housing around the DC port is designed to provide stability and prevent accidental disconnection.
By understanding these characteristics, you can easily identify the DC port on your monitor and ensure that you’re using the correct power source.
The Technical Aspects of DC Power for Monitors
Understanding the technical aspects of DC power for monitors is crucial for appreciating how these devices operate efficiently. DC power is essential for the functioning of modern monitors, and its technical details can reveal a lot about the design and performance of these devices.
The distinction between AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) power is fundamental to understanding how monitors are powered. AC power from wall outlets constantly changes direction, whereas DC power flows consistently in one direction, making it more suitable for electronic devices like monitors.
AC vs. DC Power Explained
The conversion of AC power to DC power is a critical process in powering monitors. Power adapters contain transformers and rectifiers that convert high-voltage AC power from outlets into the lower-voltage DC power that monitors require. Most modern monitors require DC power in the range of 12-24 volts, with specific amperage requirements that vary by model and screen size.
Unlike data transmission standards like DisplayPort, which send packets of information, DC power provides a continuous flow of electrical current to maintain the monitor’s operation. As
“The use of DC power in monitors allows for a stable and efficient supply of power, which is essential for high-quality display performance.”
Understanding the technical difference between AC and DC power helps explain why monitors need external power adapters rather than connecting directly to wall outlets.
The conversion from AC to DC generates some heat, which is why power adapters often feel warm during operation. This process is crucial for the safe and efficient operation of monitors, highlighting the importance of DC power in modern display technology.
In summary, the technical aspects of DC power for monitors involve the conversion of AC power to DC power, the specific voltage and amperage requirements of monitors, and the role of power adapters in this process. By understanding these details, users can appreciate the complexity and efficiency of modern monitor design.
What is a DC Port on a Computer Monitor Mean
The DC port on a computer monitor plays a vital role in its operation, serving as the primary power input. Understanding the significance of this port is essential for troubleshooting and maintaining the device. The DC port is responsible for supplying the necessary electrical current for all monitor functions, ensuring that the device operates correctly.

While data ports like HDMI and DisplayPort transmit video and audio signals, the DC port provides the fundamental power that enables the monitor to process these signals and display images. DisplayPort, for instance, includes an auxiliary data channel used for device control and automatic configuration between source and display devices. It supports various standards, including Display Data Channel (DDC), Extended Display Identification Data (EDID), and Monitor Control Command Set (MCCS).
The Role of DC Ports in Monitor Operation
The DC port is crucial for the overall operation of the monitor. It works in conjunction with the monitor’s internal power management system to regulate electricity flow to various components, including the backlight, control board, and panel. The presence of a DC port indicates that the monitor requires an external power adapter rather than having an internal power supply with a standard AC cable connection.
- The DC port ensures a stable, consistent power supply that protects sensitive electronic components from power fluctuations that could damage the monitor.
- Understanding what a DC port means helps users recognize the difference between power-related issues and signal problems when troubleshooting monitor functionality.
- The DC port supplies the necessary electrical current for all monitor functions, making it a critical component of the device.
In summary, the DC port is essential for the proper functioning of a computer monitor. It provides the necessary power for the device to operate, working in conjunction with the internal power management system to regulate electricity flow. By understanding the role of the DC port, users can better troubleshoot issues and maintain their monitors effectively.
Benefits of DC Power in Computer Monitors
The use of DC power in computer monitors offers several benefits that enhance user experience and efficiency. As technology advances, the importance of efficient power delivery systems in monitors has become increasingly evident.
Energy Efficiency Advantages
One of the primary benefits of DC power in monitors is its energy efficiency. The generation of direct current (DC) rather than alternating current (AC) is generally more efficient for small electronic devices, resulting in negligible power wastage.
- DC power delivery offers superior energy efficiency compared to AC power, resulting in less electricity consumption and lower operating costs for monitor users.
- The controlled nature of DC power helps extend the lifespan of monitor components by providing stable voltage that prevents power surges and electrical stress.
- Modern energy efficiency standards for monitors are designed around DC power systems, allowing manufacturers to meet increasingly stringent environmental regulations.
These advantages contribute to the growing adoption of DC power in modern monitors. Additionally, DC-powered monitors generate less heat during operation, which contributes to better performance and reliability, especially in professional environments where monitors run for extended periods.
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | DC power reduces electricity consumption and operating costs. |
| Component Longevity | Stable DC voltage prevents power surges and electrical stress. |
| Reliability | DC-powered monitors generate less heat, improving performance. |
As stated by a leading industry expert, “The shift towards DC power in monitors is a significant step towards achieving energy efficiency and reducing environmental impact.” This underscores the importance of adopting DC power technology in modern devices.

The external power adapter design in DC-powered monitors allows for easier replacement if power issues occur, without requiring disassembly of the monitor itself. Furthermore, DC power enables more precise voltage regulation, which is particularly important for high-performance monitors used in color-critical applications like graphic design and video editing.
DC Ports vs. Data Ports: Understanding the Difference
The world of computer monitors involves various ports, but two types stand out: DC ports for power and data ports like HDMI and DisplayPort for signal transmission. Understanding the distinction between these ports is crucial for the proper operation and troubleshooting of monitor issues.
DC ports serve a fundamentally different purpose than data ports. While HDMI and DisplayPort transmit digital video and audio data between devices, DC ports provide the electrical power necessary for the monitor to function. This difference in purpose is reflected in their design and functionality.

Comparing DC Ports to HDMI and DisplayPort
Data ports like HDMI and DisplayPort operate at high speeds to handle the bandwidth requirements of video transmission, whereas DC ports maintain a constant voltage and current for power delivery. The physical design of DC ports, typically circular, differs significantly from the rectangular shape of HDMI and DisplayPort connectors, preventing incorrect connections.
Understanding the roles of these ports is essential when troubleshooting monitor issues. Problems with display quality typically relate to data ports, while power-related issues involve the DC port. The table below summarizes the key differences between DC ports and data ports like HDMI and DisplayPort.
| Port Type | Purpose | Design | Speed/ Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|---|
| DC Port | Power Delivery | Circular | Constant Voltage/Current |
| HDMI | Video/Audio Transmission | Rectangular | High Speed |
| DisplayPort | Video/Audio Transmission | Rectangular | High Speed |
In summary, DC ports and data ports serve distinct purposes on a computer monitor. While DC ports are designed for reliable power delivery, data ports like HDMI and DisplayPort are engineered for high-speed data transmission. Recognizing these differences is key to effectively using and troubleshooting monitors.
Types of Monitor Ports: A Comprehensive Overview
Modern computer monitors come equipped with a variety of ports to cater to different video and audio transmission needs. This diversity in ports is a response to the evolving demands for higher quality displays and faster data transfer rates.
Video and Audio Transmission Ports
The most common ports found on modern monitors include HDMI, DisplayPort, and USB-C, each serving distinct purposes in video and audio transmission. HDMI (High-Definition Multimedia Interface) is widely used for its ability to transmit both video and audio through a single cable, making it a convenient option for connecting PCs, gaming consoles, and media players.

DisplayPort stands out for its capability to support higher resolutions and refresh rates, making it particularly advantageous for professional and gaming applications. It also allows for daisy-chaining multiple monitors, enhancing productivity and multitasking capabilities.
In contrast, legacy ports like DVI (Digital Visual Interface) and VGA (Video Graphics Array) are still found on some monitors, primarily for backward compatibility. However, they lack the ability to transmit audio and support for the highest resolutions.
| Port Type | Video Transmission | Audio Transmission | Max Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDMI | Yes | Yes | Up to 8K |
| DisplayPort | Yes | Yes | Up to 8K |
| USB-C | Yes | Yes | Up to 4K |
| DVI | Yes | No | Up to 2560×1600 |
| VGA | Yes | No | Up to 2048×1536 |
For more detailed information on different types of monitor ports, you can visit Xenarc’s guide on monitor ports, which provides a comprehensive overview of the various options available.
Power Adapters for Monitor DC Ports

The compatibility of a power adapter with a monitor’s DC port is a critical consideration. Ensuring that the adapter matches the monitor’s requirements is vital to prevent damage and ensure optimal performance.
Choosing the Right Power Adapter
When selecting a monitor power adapter, several factors must be considered to ensure compatibility. The voltage and amperage of the adapter must match the specifications of the monitor’s DC port. These details are usually found near the power port on the monitor or in the user manual.
Key Considerations:
- Selecting the correct power adapter requires matching three critical specifications: voltage, amperage, and connector size.
- Using an adapter with incorrect voltage can damage the monitor’s internal components.
- Most monitor power adapters provide output in the range of 12-24 volts DC, with amperage requirements varying based on the monitor’s size and features.
- The physical connector size must match the monitor’s DC port exactly.
- Manufacturer-specific adapters are generally recommended over generic replacements.
- When replacing a monitor power adapter, it’s crucial to check both the adapter’s output specifications and the monitor’s input requirements.
By focusing on these critical aspects, users can ensure they select a power adapter that is compatible with their monitor’s DC port, thereby safeguarding the device and ensuring reliable operation.
Common Issues with DC Ports on Monitors
DC ports on computer monitors are susceptible to several issues that can impact their operation. These problems can range from simple connection issues to more complex hardware faults. Understanding these common issues is crucial for troubleshooting and maintaining your monitor’s performance.
One of the most prevalent problems with DC ports on monitors is related to the connection. Loose connections between power adapters and DC ports can cause intermittent power supply or prevent the monitor from turning on altogether. Ensuring a secure connection is vital for reliable operation.
Troubleshooting Power Problems
When experiencing issues with the DC port, the first step is to troubleshoot thepowersupply. This involves checking the physicalconnection, testing with a known workingadapter, and inspecting for visible damage to both the port andconnectors. Some common problems include:
- Physical damage to the DC port connector, such as bent pins or enlarged sockets, which can lead to unreliable power delivery.
- Power adapters with frayed cables or damaged connectors, which pose both reliability and safety concerns.
- Monitors that power on but shut down unexpectedly, potentially due to issues with the DC port connection or insufficient power from an incompatible adapter.
In cases where the DC port itself is damaged, professional repair is often required as this typically involves soldering components on the monitor’s internal circuit board.
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Intermittent Power | Loose connections | Secure the connection |
| Monitor won’t turn on | Damaged DC port or adapter | Inspect and replace damaged components |
| Unexpected shutdown | Incompatible or faulty adapter | Test with a compatible adapter |
By understanding these common issues and following the troubleshooting steps, users can often resolve problems with their monitor’s DC port. Regular maintenance, such as checking the condition of the power adapter and ensuring secure connections, can help prevent many of these issues.

DC Port Specifications Across Different Monitor Brands
DC port specifications can vary significantly across different monitor brands, making it essential to understand these differences. While HDMI and DVI standards are universally consistent across brands, DC port specifications can differ significantly between monitor manufacturers.
Most monitor brands use standard barrel-type DC connectors, but the exact dimensions (diameter and pin size) differ based on the manufacturer’s specifications. Common DC port configurations include 5.5mm × 2.5mm, 5.5mm × 2.1mm, and 4.0mm × 1.7mm connectors, with the first number representing the outer diameter and the second representing the inner pin diameter.
Standard DC Port Configurations
Beyond physical dimensions, voltage requirements also vary across brands. For instance, Dell monitors typically use 19.5V, HP monitors often require 12V, and other brands use various voltages between 12V and 24V. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the correct replacement power adapters.
Some premium monitor brands implement proprietary DC connector designs to ensure users purchase brand-specific replacement adapters rather than generic alternatives. This highlights the importance of understanding the specific DC port standards used by different monitor brands.
| Monitor Brand | Common DC Port Configuration | Typical Voltage Requirement |
|---|---|---|
| Dell | 5.5mm × 2.5mm | 19.5V |
| HP | 5.5mm × 2.1mm | 12V |
| Other Brands | 4.0mm × 1.7mm | 12V-24V |
When comparing DC ports across different monitor brands, it’s clear that while some standards exist, variations are common. This table summarizes some of the common configurations and voltage requirements.

In conclusion, understanding the DC port specifications across different monitor brands is essential for ensuring compatibility and safety when using or replacing power adapters. By recognizing the variations in DC port configurations and voltage requirements, users can make informed decisions.
How to Properly Connect Power to Your Monitor
A proper power connection is essential for your monitor to function correctly. Ensuring your monitor is powered correctly is the first step in setting up your workstation. This involves understanding the different types of connections and cables used for power and video transmission.

Step-by-Step Connection Guide
To connect power to your monitor, follow these steps carefully:
- Ensure both the monitor and the power source are turned off before making any connections to prevent electrical surges.
- Identify the DC port on the back of your monitor, typically labeled as “DC IN” or marked with a power symbol, distinguishing it from video input ports like HDMI or DVI.
- Align the power adapter’s connector with the DC port, ensuring the correct orientation to avoid damaging the port or the connector.
- Gently but firmly insert the power adapter connector into the DC port until it’s fully seated.
- Connect the other end of the power adapter to a wall outlet or a power strip, preferably one with surge protection.
- Once the power connection is secure, turn on the monitor and verify that the power indicator light is on, confirming a stable power connection.
- Finally, connect your video cables (HDMI, DVI, or DisplayPort) to complete the setup.
By following these steps, you can ensure a safe and proper power connection for your monitor, setting it up for optimal performance.
As “A well-connected monitor is the foundation of a productive workstation.” Properly connecting your monitor not only ensures it functions correctly but also contributes to the overall efficiency of your work environment.
DC Ports in Modern Monitor Designs
The design of DC ports in modern monitors reflects a balance between aesthetics and functionality. As monitors become slimmer and more feature-rich, the placement and design of DC ports have evolved to maintain clean aesthetics while ensuring secure connections.
Modern monitor designs have incorporated more efficient and versatile power delivery systems. DC ports remain the standard, but with improvements in design and functionality. For instance, some high-end monitors now feature detachable power cables between the adapter and the DC port, allowing for easier cable management and replacement if damaged.
Evolution of Power Delivery in Monitors
The evolution of power delivery in monitors has been influenced by advancements in display technology, such as the development of DisplayPort version 1.2, introduced on January 7, 2010. This version doubled the data rate to 17.28 Gbit/s in High Bit Rate 2 (HBR2) mode, enabling increased resolutions, higher refresh rates, and greater color depth, such as 3840 × 2160 at 60Hz 10bpc RGB.
As DisplayPort technology has evolved to support higher resolutions and refresh rates, the power requirements delivered through DC ports have also increased to support these advanced display capabilities. This has led to improvements in DC port design to handle the increased power transmission requirements.
| Feature | DisplayPort 1.2 | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Data Rate | 17.28 Gbit/s | Higher resolutions and refresh rates |
| Multi-Stream Transport | Supported | Daisy-chain connection with multiple devices |
| AUX Channel Bandwidth | Up to 720 Mbit/s | Improved transmission capabilities |
Furthermore, USB-C is emerging as an alternative to traditional DC ports in some monitor designs, offering the ability to transmit both power and video signals through a single connection way. Despite these innovations, dedicated DC ports remain the most common and reliable way to deliver power to monitors, especially for larger displays with higher power requirements.
Alternative Power Options for Monitors
With the rise of USB-C, monitors now have versatile alternatives for powering up. This shift is driven by the need for simpler, more efficient connectivity solutions that can handle both power delivery and data transmission.
USB-C Power Delivery for Monitors
USB-C with Power Delivery (PD) is emerging as a significant alternative to traditional DC ports, allowing a single cable to transmit both power and video signals to compatible monitors. The USB-C PD standard can deliver up to 100 watts of power, sufficient for most monitors except the largest and most power-hungry professional displays.
Some key benefits of USB-C PD for monitors include:
- Simplified connectivity with a single cable for both power and data
- Compatibility with a wide range of devices, from laptops to portable power banks
- Enhanced flexibility for different setup requirements and connection preferences
Portable monitors designed for travel often utilize USB-C power, drawing electricity directly from the connected laptop or portable power bank without requiring a separate power adapter. Some modern monitors feature both traditional DC ports and USB-C power options, providing flexibility for different setup requirements.
Battery-powered monitors represent another alternative power option, particularly useful for field work, presentations, or situations where wall power is unavailable. As power delivery technology evolves, we’re seeing increased integration between power and data connections, potentially reducing the need for separate DC ports in future monitor designs.
The adoption of USB-C PD for monitors signifies a move towards more streamlined and efficient power and data connectivity. As this technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative applications in the realm of monitor power delivery.
DC Ports and Monitor Performance
The quality of the DC port connection has a profound impact on a monitor’s ability to render video at high refresh rates and higher resolutions. A stable power delivery through a properly functioning DC port is essential for maintaining consistent monitor performance, particularly for displays operating at high refresh rates or resolutions.

For gaming monitors with high refresh rates such as 120Hz, 144Hz, or 240Hz, the importance of a proper DC port connection cannot be overstated. These monitors have increased power requirements compared to standard displays. Insufficient or unstable power can cause various display issues, including screen flickering, inconsistent brightness, color shifting, or complete failure to maintain video output.
How Power Affects Display Quality
The quality and stability of a monitor’s display are significantly influenced by the power it receives. While HDMI and other video connections determine what content can be displayed, the quality and stability of that content’s presentation depend significantly on clean, consistent power through the DC port.
Professional monitors used for color-critical work require extremely stable power to maintain precise color accuracy and brightness levels throughout extended use. Power fluctuations through damaged or loose DC port connections can reduce a monitor’s effective lifespan by stressing internal components and power regulation systems.
In summary, a properly functioning DC port is crucial for optimal monitor performance, especially for high-demand applications like gaming and professional color grading. Ensuring stable power delivery will help maintain the quality and longevity of the display, providing a better video viewing experience.
Future Trends in Monitor Power Technology
Monitor power technology is poised for a significant transformation, driven by emerging standards and innovations. As displays continue to advance in terms of resolution and refresh rates, the power requirements are also changing. The future of monitor power technology is moving toward greater integration between power and data connections.
Standards like USB4 and Thunderbolt are combining DisplayPort video signals with power delivery in a single cable, simplifying connectivity and reducing clutter. This integration is expected to become more prevalent, making it easier to power and connect monitors to computers.
Emerging Standards and Innovations
The evolution of display standards, such as DisplayPort and HDMI, is driving the need for more efficient power delivery. As monitors support higher resolutions and refresh rates beyond what current standards can deliver, power requirements will increase accordingly. This may necessitate new DC port designs with higher capacity.
- The development of DisplayPort 1.4 has added support for Display Stream Compression (DSC) and Forward Error Correction, enhancing the capabilities of current display technology.
- Energy efficiency innovations are driving the development of monitors that require less power while delivering better performance, potentially changing the specifications for DC power delivery.
- The obsolescence of legacy video standards like DVI in favor of DisplayPort and HDMI is paralleled by evolution in power delivery methods.
Industry standardization efforts may eventually lead to more universal power adapter specifications for monitors, similar to how USB-C has standardized charging for many mobile devices. This could simplify the user experience and reduce electronic waste.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the significance of DC ports on computer monitors extends beyond just power delivery. Understanding the DC port and other types of monitor ports can significantly improve your setup experience, ensuring optimal performance and longevity for your equipment.
The DC port serves the critical function of delivering power to the display, working alongside but distinctly from data ports like DisplayPort and HDMI that transmit video and audio signals. Proper understanding of DC port specifications ensures users can select compatible power adapters that match voltage, amperage, and connector requirements for their specific monitor model.
As monitor technologies continue to advance, supporting higher resolutions, faster refresh rates, and enhanced color capabilities, the importance of stable power delivery through properly functioning DC ports becomes increasingly significant. Emerging technologies like USB-C are offering alternative power delivery methods, simplifying cable management by combining power and data transmission.
By distinguishing between power-related problems and signal-related problems, users can efficiently troubleshoot monitor issues. The future of monitor power technology will likely evolve with greater standardization, improved energy efficiency, and more integrated connection options, simplifying the user experience while supporting demanding performance requirements for gaming, professional, and general-use applications.
FAQ
What does DC power mean for a computer monitor?
DC power refers to the type of electrical current used to power devices like monitors. Unlike AC power, DC power provides a stable voltage, making it suitable for electronic devices.
How do I identify a DC port on my monitor?
A DC port is typically marked with a symbol indicating DC power input, and it’s usually a barrel connector or a similar type of connector. Check your monitor’s manual or manufacturer’s website for specific information.
Can I use any power adapter with my monitor’s DC port?
No, you should use a power adapter that matches the monitor’s DC port specifications, including voltage and current ratings, to avoid damaging the device.
What is the difference between a DC port and data ports like HDMI or DisplayPort?
DC ports are used for power delivery, while data ports like HDMI and DisplayPort are used for transmitting video and audio signals between devices.
How does DC power affect monitor performance?
A stable DC power supply ensures optimal monitor performance, including display quality and refresh rates. Inadequate power can lead to issues like flickering or dimming.
Are there alternative power options for monitors besides traditional DC ports?
Yes, some modern monitors support USB-C Power Delivery, which can supply both power and data through a single cable, offering greater convenience and reduced clutter.
What are the benefits of using DC power in computer monitors?
DC power provides energy efficiency advantages, as it allows for more efficient power conversion and reduced heat generation, leading to longer device lifespan.
Can a faulty DC port cause issues with my monitor’s display quality?
Yes, a faulty DC port or inadequate power supply can cause display issues, such as flickering, dimming, or failure to turn on.
How do I troubleshoot power problems with my monitor’s DC port?
Check the power cord, adapter, and DC port for damage or debris. Try using a different power adapter or cord to isolate the issue.
Are DC port configurations standardized across different monitor brands?
While there are standard DC port configurations, some monitor brands may use proprietary connectors or specifications, so it’s essential to check the manufacturer’s documentation.















