How to Know if My Computer Has a Thunderbolt Port: A Guide
Identifying whether your device has a Thunderbolt port is crucial for unlocking enhanced connectivity and performance capabilities. In today’s tech landscape, Thunderbolt technology offers faster data transfer speeds and versatile connectivity options, making it an essential feature for users who rely on external displays, high-speed storage, and other peripherals.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of identifying Thunderbolt ports on both Windows and Mac systems. By the end of this article, you will be able to determine whether your computer is equipped with a Thunderbolt port and understand the benefits of using this advanced technology with the right cable and devices.
Understanding Thunderbolt Technology
Developed by Intel in collaboration with Apple, Thunderbolt technology offers unparalleled speed and versatility. It’s a powerful and versatile connectivity technology that allows for high-speed data transfer, video output, and power delivery through a single port.
What is Thunderbolt Technology?
Thunderbolt is a high-performance I/O solution designed to connect various peripherals to your computer. It combines PCIe, DisplayPort, and power delivery in a single connection, making it superior to standard USB connections. This technology is particularly useful for users who need to transfer large files or connect multiple devices.
Evolution of Thunderbolt: Versions 1 Through 5
The evolution of Thunderbolt has been marked by significant improvements in speed. From Thunderbolt 1 (10 Gbps) to Thunderbolt 5 (80 Gbps), each generation has offered faster data transfer rates. Thunderbolt 5 ports are available on newer Mac models, such as the Mac Studio introduced in 2025 and certain MacBook Pro models introduced in 2024.
Thunderbolt vs. USB-C: Key Differences
While Thunderbolt and USB-C share the same connector shape, they offer different capabilities. Thunderbolt ports can support higher speeds and multiple protocols, including PCIe and DisplayPort. When using a USB-C cable with a Thunderbolt port, the connection will work, but it won’t offer the same speeds as a Thunderbolt device. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the right device and cable for your needs.
In conclusion, Thunderbolt technology is a versatile and powerful connectivity solution that offers high-speed data transfer, video output, and power delivery. Its compatibility with various devices and computers, including those running Windows, makes it a valuable feature to consider when selecting a computer.
Physical Identification of Thunderbolt Ports
The first step in harnessing the power of Thunderbolt is understanding how to identify a Thunderbolt port. Thunderbolt ports are designed to be easily recognizable, but their appearance can vary slightly depending on the device and the generation of Thunderbolt technology.
Thunderbolt Port Symbols and Markings
Thunderbolt ports are typically marked with a distinctive lightning bolt symbol. This symbol is a universal indicator that the port supports Thunderbolt technology. On some devices, particularly those with Thunderbolt 3 or later, the port might be labeled with a “TB” or “Thunderbolt” logo. For instance, on iMac models from 2021 or later, the Thunderbolt symbol is displayed above each Thunderbolt/USB4 port, indicating its capability.
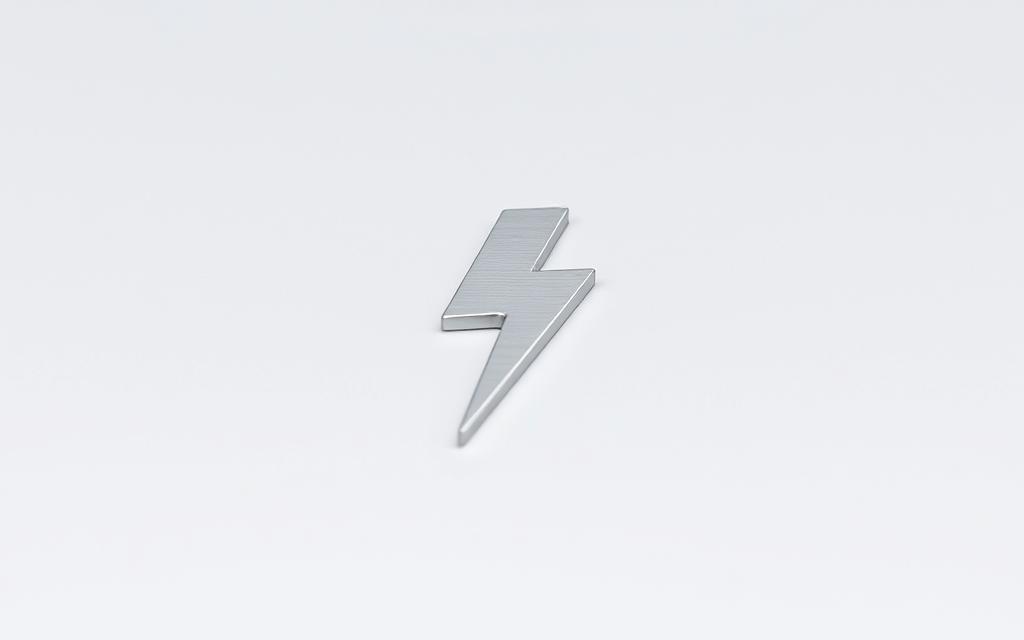

Common Locations of Thunderbolt Ports on Laptops and Desktops
Thunderbolt ports can be found in various locations on laptops and desktops. On laptops, they are often located on the sides or edges, while on desktops, they are typically found on the rear panel. Knowing these common locations can help you quickly identify Thunderbolt ports on your device.
Visual Differences Between Thunderbolt and Similar Ports
One of the challenges in identifying Thunderbolt ports is distinguishing them from other similar-looking ports, such as USB-C or Mini DisplayPort. While Thunderbolt 3 and 4 ports use the USB-C connector, not all USB-C ports support Thunderbolt. The key to differentiation lies in the symbol or logo on the port. Checking for the Thunderbolt symbol or manufacturer’s labeling can help you identify whether a USB-C port supports Thunderbolt.
By understanding these visual cues and common locations, you can easily identify Thunderbolt ports on your laptop or desktop, enabling you to take full advantage of Thunderbolt’s high-speed data transfer and display connectivity capabilities.
How to Know if My Computer Has a Thunderbolt Port on Windows

Checking if your Windows computer has a Thunderbolt port is a straightforward process that involves a few simple steps. To start, you’ll need to verify the presence of a Thunderbolt controller using the Device Manager.
Using Device Manager to Identify Thunderbolt Controllers
To check for a Thunderbolt port, open the Device Manager by searching for it in the Start menu. Once open, expand the “System devices” category and look for “Thunderbolt Controller.” If it’s listed, your computer has a Thunderbolt port. Ensure there are no warning signs on the controller, as these may indicate a problem with the port or its driver.
Checking System Information for Thunderbolt Support
Another way to verify Thunderbolt support is by using the System Information utility. Type “msinfo32” in the Run dialog box (Windows key + R) to open it. In the System Information window, look for entries related to Thunderbolt under the “Components” or “System Devices” sections. This can provide details about the Thunderbolt hardware and driver installation status.
Using Thunderbolt Control Center on Windows
For more detailed management of Thunderbolt devices and security settings, you can download and install the Thunderbolt Control Center from the official Intel website or your computer manufacturer’s support page. This tool allows you to configure Thunderbolt settings and check for firmware updates.
For more information on checking Thunderbolt ports, you can visit this guide for detailed instructions.
Identifying Thunderbolt Ports on Mac Computers
To harness the full potential of your Mac, it’s essential to know how to identify its Thunderbolt ports. Thunderbolt ports offer high-speed data transfer, connectivity to external devices, and the ability to daisy-chain multiple peripherals. Mac computers come with various Thunderbolt generations, and understanding these differences is key to maximizing your device’s capabilities.
Using “About This Mac” to Find Port Information
One of the simplest ways to identify if your Mac has Thunderbolt ports is by using the “About This Mac” feature. To do this, click on the Apple menu and select “About This Mac.” Then, double-click on your model name, and press Command-C to copy it. Next, go to the Tech Specs page on Apple’s website, click on the Search Tech Specs bar, and press Command-V to paste your model name. Click Search, and then click on the specs page for your Mac. This process will provide detailed information about your Mac’s ports, including Thunderbolt ports.
Checking Mac Model Specifications
Different Mac models support different generations of Thunderbolt. For instance, the Mac Studio introduced in 2025 and the 14-inch MacBook Pro with M4 Pro or M4 Max chip introduced in 2024 feature Thunderbolt 5. On the other hand, MacBook Air introduced in 2025 and iMac introduced in 2024 come with Thunderbolt 4. Understanding the specifications of your Mac model is crucial for determining the type and generation of Thunderbolt ports it supports.
Identifying Thunderbolt Generations on Different Mac Models
Mac models have evolved over the years, incorporating various generations of Thunderbolt ports. The transition from Thunderbolt 1 and 2, which used Mini DisplayPort shapes, to Thunderbolt 3, 4, and 5, which use USB-C shapes, has been significant. For example, Intel-based MacBook Pro models introduced between 2016 and 2020 feature Thunderbolt 3, while newer models like the 14-inch MacBook Pro with M3 introduced in 2023 support Thunderbolt / USB4. A detailed breakdown of Thunderbolt generations across different Mac models is as follows:
| Mac Model | Thunderbolt Generation | Introduction Year |
|---|---|---|
| Mac Studio | Thunderbolt 5 | 2025 |
| 14-inch MacBook Pro with M4 Pro/M4 Max | Thunderbolt 5 | 2024 |
| MacBook Air | Thunderbolt 4 | 2025 |
| iMac | Thunderbolt 4 | 2024 |
| 14-inch MacBook Pro with M3 | Thunderbolt / USB4 | 2023 |
By following these steps and understanding the specifications of your Mac, you can easily identify the type and generation of Thunderbolt ports on your device, ensuring you maximize its connectivity and productivity capabilities.
Testing if Your Thunderbolt Port is Working Properly
You can determine if your Thunderbolt port is working by following a few simple steps. First, ensure that your Thunderbolt device is properly connected to the port. A loose connection can lead to malfunctioning or failure to recognize the device.

Connecting Thunderbolt Devices to Verify Functionality
To test the functionality of your Thunderbolt port, connect a compatible Thunderbolt device such as an external drive, dock, or display. If the device is recognized by your computer, it indicates that the port is working. On a Windows device, you can verify this by checking the Device Manager for the connected device.
Troubleshooting Connection Issues
If your Thunderbolt device is not recognized, troubleshoot the connection by checking the cable for any damage or issues. Ensure that the Thunderbolt port is enabled in your computer’s settings. You can also update the Thunderbolt controller driver to the latest version to resolve any compatibility issues.
Using Diagnostic Tools to Test Thunderbolt Ports
Both Windows and Mac offer built-in diagnostic tools to test the functionality of your Thunderbolt port. On Windows, use the Device Manager to check for any errors or warnings related to the Thunderbolt controller. For Mac, you can use the System Report to verify the Thunderbolt configuration. These tools help identify any issues with the port or connected devices.
By following these steps, you can effectively test and troubleshoot your Thunderbolt port to ensure it is working correctly and efficiently.
Common Thunderbolt Port Issues and Solutions
Common issues with Thunderbolt ports can be frustrating, but understanding their causes is the first step to resolving them. Thunderbolt technology, known for its high-speed data transfer and versatility, can sometimes present challenges for users.
Driver and Firmware Update Problems
Outdated or incompatible drivers can cause issues with Thunderbolt ports. To update the Thunderbolt drivers on a Windows system, you can follow these steps: Right-click on the Thunderbolt controller entry in Device Manager, select “Update driver,” and choose to search automatically for updated driver software. Once the drivers are updated, restart your computer and check if the Thunderbolt port is working.
Connection and Recognition Issues
Connection problems can arise due to faulty cables or incorrect device configuration. Ensure that you’re using a certified Thunderbolt cable and that the device is properly connected. If the issue persists, try restarting both the computer and the Thunderbolt device.

Power Delivery Complications
Power delivery issues can occur if the Thunderbolt port is not receiving sufficient power or if there’s a problem with the power supply. Check that your device is properly connected to a power source and that the cable is not damaged.
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Driver Update Problems | Outdated or incompatible drivers | Update drivers via Device Manager |
| Connection Issues | Faulty cables or incorrect configuration | Check cable and device connection |
| Power Delivery Complications | Insufficient power supply | Check power source and cable condition |
By understanding and addressing these common issues, users can troubleshoot and resolve problems with their Thunderbolt ports, ensuring optimal performance and functionality.
Maximizing Your Thunderbolt Port Capabilities
The versatility of Thunderbolt ports allows users to expand their computer’s capabilities in multiple ways. By understanding the full potential of Thunderbolt technology, users can significantly enhance their productivity and workflow.
Connecting Multiple Displays
One of the key benefits of Thunderbolt is its ability to support multiple displays from a single port. This feature is particularly useful for professionals who require a multi-monitor setup for tasks such as video editing, graphic design, or software development. When connecting multiple displays, it’s essential to consider the resolution and refresh rate supported by your Thunderbolt port and monitors.

Daisy-Chaining Thunderbolt Devices
Thunderbolt technology supports daisy chaining, allowing users to connect multiple devices in series using a single Thunderbolt cable. To daisy chain devices, ensure each device has two Thunderbolt ports (input and output), then connect the devices sequentially.
High-Speed Data Transfer Applications
Thunderbolt’s high-speed data transfer capabilities make it ideal for applications involving large files, such as video editing and 3D rendering. By leveraging Thunderbolt, professionals can significantly reduce the time spent transferring files between devices.
| Application | Transfer Speed | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Video Editing | Up to 40 Gbps | Reduced file transfer time |
| 3D Rendering | Up to 40 Gbps | Improved workflow efficiency |
Conclusion: Ensuring Your Thunderbolt Experience
Identifying Thunderbolt ports is the first step to enhancing your computing experience. By understanding how to check for Thunderbolt ports on your Windows or Mac computer, you can maximize your device’s capabilities. To ensure you’ve correctly identified your Thunderbolt port, revisit the key methods outlined in this guide. This includes checking for specific symbols, using Device Manager on Windows, or checking your Mac’s specifications. As Thunderbolt technology continues to evolve, being aware of the latest developments will help you make the most of your Thunderbolt devices. Explore the full potential of your Thunderbolt port and discover the benefits of high-speed data transfer and multiple display connections.
FAQ
What is the difference between Thunderbolt and USB-C ports?
Thunderbolt and USB-C ports may look similar, but Thunderbolt ports offer faster speeds and the ability to connect multiple devices, whereas USB-C ports are more versatile but generally slower. Thunderbolt 3 and 4 use the USB-C connector, but not all USB-C ports support Thunderbolt.
How can I identify a Thunderbolt port on my laptop or desktop?
Thunderbolt ports are typically marked with a lightning bolt symbol. You can also check your device’s documentation or manufacturer’s website for specifications. On Windows, you can use Device Manager to look for Thunderbolt controllers.
Can I use a USB-C cable with a Thunderbolt port?
Yes, Thunderbolt 3 and 4 ports are compatible with USB-C cables, but you may not achieve Thunderbolt speeds. To get the full benefits of Thunderbolt, use a Thunderbolt-certified cable.
Why is my Thunderbolt device not being recognized by my computer?
This could be due to a variety of issues, including outdated drivers, faulty cables, or incorrect settings. Try updating your Thunderbolt drivers, checking the cable for damage, or resetting the Thunderbolt controller.
Can I connect multiple displays to a single Thunderbolt port?
Yes, Thunderbolt 3 and 4 support multi-display setups. You can daisy-chain multiple displays or use a Thunderbolt dock to expand your connectivity options.
What is the maximum data transfer speed of Thunderbolt 4?
Thunderbolt 4 offers speeds of up to 40 Gbps, making it ideal for demanding applications like video editing and data transfer.
How do I update my Thunderbolt drivers on Windows?
You can update your Thunderbolt drivers through Device Manager. Look for the Thunderbolt controller, right-click, and select “Update driver” to search for and install the latest drivers.
Are Thunderbolt ports backward compatible with older Thunderbolt versions?
Yes, Thunderbolt ports are generally backward compatible. For example, Thunderbolt 3 is compatible with Thunderbolt 2 devices using an adapter, but you may not achieve the same speeds as native Thunderbolt 3 devices.