New PC Won’t Connect to LAN? Likely Port Issues Explained
When a computer fails to connect to a Local Area Network (LAN), it can be a source of significant frustration. Many users experience difficulties when their brand-new device refuses to establish a network connection despite seemingly correct settings.
The issue often lies in the physical and data link layers of the network stack, particularly with port-related problems. Understanding whether the issue stems from hardware failures or software configuration problems is crucial for efficient troubleshooting on Windows computers.
This comprehensive guide will walk through the systematic diagnosis of LAN connection issues, focusing on port issues that commonly affect Windows computers, providing practical solutions that don’t require advanced technical expertise.
Understanding LAN Connectivity Problems in New PCs
Understanding the root causes of LAN connectivity failures in new PCs is crucial for resolving the issue. LAN connectivity issues can arise from various factors, including hardware malfunctions, incorrect configurations, and port problems.
Common Symptoms of LAN Connection Failures
New PCs often display specific symptoms when experiencing LAN connection failures. These include “No network access” warnings, limited connectivity notifications, or the network icon showing an exclamation mark in Windows. The most common indicators of LAN connectivity problems include the inability to access shared network resources, failure to obtain an IP address, and Windows reporting “Identifying network” without progressing further.
Why Port Issues Are Often the Culprit
Port issues frequently cause these problems because new computers may have driver incompatibilities, default security settings blocking connections, or physical connection problems that weren’t properly tested before shipping. This can lead to issues with the ethernet connection, resulting in a failure to connect to the network.
Overview of Network Ports: Physical vs. Logical
Network ports refer to the physical connectors on devices such as switches, routers, and PCs, as well as the logical ports used by network protocols. Physical ports are the actual hardware interfaces like ethernet ports on your computer and router, while logical ports are software-defined communication channels used by network protocols. Understanding this distinction is crucial because troubleshooting physical port issues requires different approaches than addressing logical port problems.
Physical Port Issues That Prevent LAN Connections
Physical port issues can be a significant obstacle to establishing a stable LAN connection. When a new PC or device is unable to connect to the network, it is often due to problems with the physical ports on the device or the networking equipment.
Faulty or Damaged Ethernet Cables
A damaged or faulty ethernet cable can prevent a stable connection. To identify the issue, inspect the cable for bent connectors, visible wire damage, or cables that don’t “click” properly when connected to ports. Testing with a known working ethernet cable is one of the simplest yet most effective troubleshooting steps.
Network Interface Card (NIC) Hardware Problems
NIC hardware problems are common in new PCs and can manifest as Windows recognizing the hardware but failing to establish a connection. Symptoms include lights not illuminating on the port or intermittent connectivity. Checking the status lights on the NIC can help identify potential hardware failures.
Router and Switch Port Malfunctions
Router and switch port malfunctions can prevent LAN connections even when the computer is properly configured. Check for status lights on both the router port and computer network card to identify potential hardware failures.
Port Speed and Duplex Mismatches
A mismatch in port speed or duplex settings between the PC and the switch can cause connectivity problems. This is particularly common with newer computers connecting to older networking equipment. Ensuring that the port settings are compatible can resolve the issue.
| Issue | Symptoms | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Faulty Ethernet Cable | No connection, intermittent connectivity | Inspect and replace the cable |
| NIC Hardware Problems | Lights not illuminating, Windows recognizes hardware but fails to connect | Check NIC status lights, replace if necessary |
| Router/Switch Port Malfunctions | No connection, status lights not illuminating | Check status lights, restart or replace router/switch |
| Port Speed/Duplex Mismatches | Slow or unstable connections | Ensure compatible port settings |

If New PC Can’t Connect to LAN: What Port Issue Is Most Likely?
If your new PC won’t connect to the LAN, it’s likely due to a problem with the network port. The most common issue in such cases is related to the network drivers. When the hardware is connected but the drivers are missing or corrupted, Windows cannot properly communicate with the network hardware, despite the physical connection being intact.
Identifying Missing or Corrupted Network Drivers
Missing or corrupted network drivers are a frequent cause of LAN connectivity issues on new computers. To identify such problems, you should check the Device Manager for devices with yellow exclamation marks or “Unknown devices” under the Network Adapters section. Driver issues typically manifest in this manner, indicating that Windows is unable to properly utilise the network hardware.
To check for driver issues, open the Device Manager by pressing Win+R and typing “devmgmt.msc”. Look for the Network Adapters section and inspect the devices listed there. If you find a device with a warning symbol or a generic name like “Ethernet Controller”, it may indicate a driver problem.
Using Device Manager to Diagnose Network Adapter Issues
The Device Manager is a crucial tool for diagnosing network adapter issues. By examining the Network Adapters section, you can identify devices that are not functioning correctly. Right-clicking on the problematic device and selecting “Properties” provides more detailed information about the issue.
To diagnose network adapter issues effectively, ensure you follow the steps outlined in the previous section. Checking the device properties can give you insights into whether the problem is driver-related.
Finding Hardware IDs for Proper Driver Installation
When standard driver installation methods fail, identifying the exact hardware using the Hardware ID can be very helpful. To find the Hardware ID, go to the “Details” tab in the device properties and select “Hardware Ids” from the Property dropdown menu. The Hardware ID, which looks like “PCI\VEN_xxxx&DEV_xxxx”, can be searched online to find the appropriate driver.
This method is particularly useful for new computers where the manufacturer may not have included all necessary drivers, or when Windows Update cannot locate the correct network adapter driver. By using the Hardware ID, you can ensure that you install the correct driver for your network adapter, resolving the LAN connectivity issue.
Troubleshooting and Resolving LAN Port Issues
When a new PC fails to connect to the LAN, it is often due to port issues that can be resolved through systematic troubleshooting. LAN connectivity problems can arise from various sources, including hardware faults, driver issues, and configuration problems.
Running Windows Network Troubleshooter
Windows includes a built-in Network Troubleshooter that can automatically detect and fix common connection problems. To access it, navigate to Start Menu > Settings > Network & Internet > Status > Network troubleshooter.
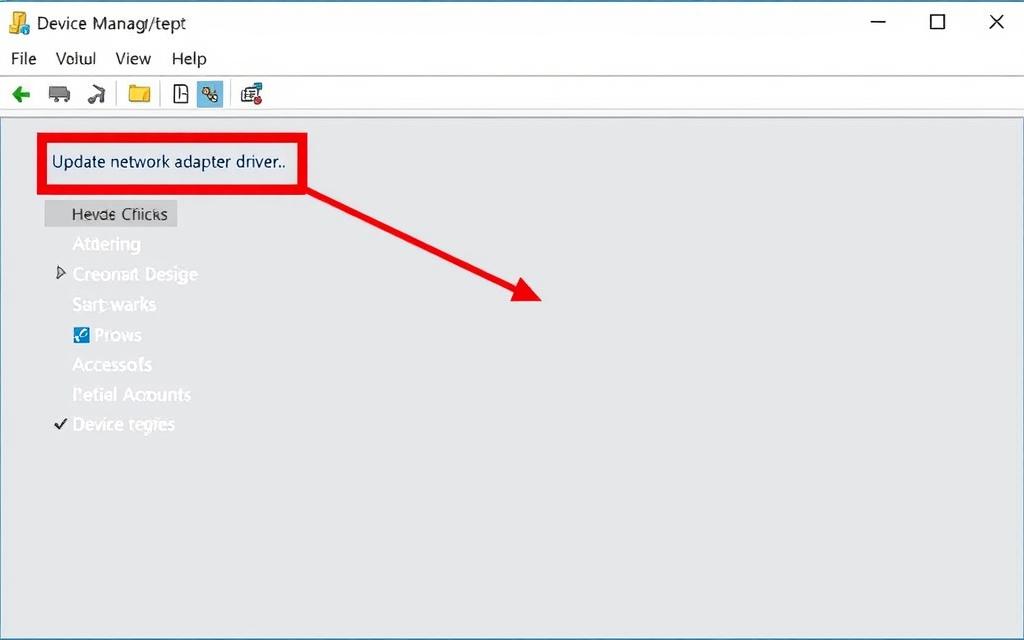
Checking and Updating Network Adapter Drivers
For driver-related issues, use Device Manager to update network adapter drivers. Right-click the adapter, select “Update driver,” and choose to search automatically or browse your computer for driver software.
Configuring Firewall Settings for LAN Access
Windows Firewall or third-party security software often blocks LAN connections on new computers. Check your firewall settings to ensure that private network connections are allowed and that no specific blocking rules exist for local network traffic.
Resolving DHCP and DNS Port Issues
DHCP issues can prevent your computer from obtaining an IP address automatically. Verify that your router has DHCP enabled and that your computer is set to obtain IP settings automatically. DNS configuration problems can also cause connectivity issues; try setting alternative DNS servers like Google’s (8.8.8.8) to test if this resolves the issue.
By following these steps, you can identify and resolve LAN port issues on your new PC. If problems persist, consider resetting the TCP/IP stack and Winsock catalog using Command Prompt commands like “netsh winsock reset” and “netsh int ip reset.”
Conclusion: Ensuring Stable LAN Connectivity for Your New PC
By methodically troubleshooting LAN connectivity problems, you can ensure a stable network connection. Establishing a reliable ethernet connection requires a systematic approach to identifying and resolving port-related issues.
Regular maintenance of your network setup, including checking cable connections and keeping Windows and drivers updated, can prevent many common LAN connectivity problems. Creating a network troubleshooting checklist specific to your setup can save time in future situations.
For persistent issues, consider implementing network monitoring tools that can alert you to potential port issues before they cause complete connection failures. Remember, Windows updates can occasionally cause network driver incompatibilities, so checking for driver issues should be your first step if connection problems arise after an update.
Most LAN connection issues can be resolved without professional assistance by following systematic troubleshooting approaches. If issues persist, consulting your computer or router manufacturer’s support resources can provide device-specific solutions.
FAQ
Why is my Ethernet connection not working on my computer?
The issue could be due to a faulty Ethernet cable, a malfunctioning Network Interface Card (NIC), or a problem with the router or switch. Check the cable for damage and try replacing it. Ensure the NIC is properly installed and configured.
How do I diagnose network adapter issues using Device Manager?
Open Device Manager, locate the Network Adapters section, and check for any devices with a yellow exclamation mark or a red cross. This indicates a problem with the device. You can also check the device’s properties to see if it’s disabled or if there are any error messages.
What should I do if my network drivers are missing or corrupted?
You can download the latest drivers from the manufacturer’s website, such as Intel or Realtek, and install them manually. Alternatively, you can use the Windows Update feature to search for and install the latest drivers.
How do I configure Firewall settings to allow LAN access?
Go to the Windows Defender Firewall settings, click on “Allow an app or feature through Windows Defender Firewall,” and ensure that the necessary applications are allowed through the firewall. You may need to add the application manually if it’s not listed.
What is the purpose of running the Windows Network Troubleshooter?
The Windows Network Troubleshooter is a built-in tool that can help diagnose and resolve common network connectivity issues, including those related to LAN connections. It can detect problems such as incorrect IP configurations or issues with the network adapter.
How do I check for port speed and duplex mismatches?
You can check the port speed and duplex settings in the Network Adapter properties in Device Manager. Ensure that the settings match the requirements of your network. A mismatch can cause connectivity issues or slow down your network.
What is the difference between physical and logical network ports?
Physical network ports refer to the actual Ethernet ports on a device, while logical ports are used for communication between devices over a network. Logical ports are used for specific services, such as HTTP or FTP.
How do I resolve DHCP and DNS port issues?
Check the DHCP and DNS settings on your router and ensure they are configured correctly. You can also try restarting the router or checking the IP configuration on your computer to ensure it’s obtaining the correct IP address from the DHCP server.















